Human Skeleton

WELCOME TO STRONTIUM FOR BONES BLOG
Have you experienced negative, and even dangerous, side effects from Fosamax (alendronate), Boniva (ibandronate), Actonel (risedronate), Reclast (zoledronic acid), Prolia (denosumab), Forteo (teriparatide), Tymlos (abaloparatide), or other drugs prescribed for osteoporosis? If you have, then rest assured there is a safe, effective treatment for this condition. Strontium, primarily in the form of strontium citrate, is taken orally once a day.
Visitors to my blog can leave comments or ask questions and can remain anonymous, if they wish. Their comments are relayed to my g-mail inbox. Below each post, the number of comments for that post is cited and underlined because it is a link. By clicking on that link below any post, a window opens so that a visitor can leave a comment. Ideally, visitors leave comments on posts most relevant to their comments. All comments to my posts are moderated by me.
Browse the posts and visit the link library of references.
Visitors to my blog can leave comments or ask questions and can remain anonymous, if they wish. Their comments are relayed to my g-mail inbox. Below each post, the number of comments for that post is cited and underlined because it is a link. By clicking on that link below any post, a window opens so that a visitor can leave a comment. Ideally, visitors leave comments on posts most relevant to their comments. All comments to my posts are moderated by me.
Browse the posts and visit the link library of references.
Blog Archive
Thursday, December 18, 2008
Bone Quality
Bone strength is determined by several properties, especially bone mass, which is measured using ionizing radiation (DEXA scan). Another technique used to evaluate bone strength uses ultrasound waves to describe two other properties of bone that are also related to bone strength: elasticity and structure. As the ultrasound wave passes through the heel bone (os calcis), the wave is altered. The way in which the ultrasound wave is altered describes the elasticity and structure of the bone. These two properties are combined into the term “Stiffness Index”. Studies have shown that Stiffness Index is related to bone density, making it a good indicator of bone strength.
Tuesday, December 16, 2008
U.S. National Library of Medicine (NLM)
I have asked the U.S. National Library of Medicine (NLM) to add strontium citrate to their list of alternative therapies for osteoporosis. To contact the agency, use http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/osteoporosis.html.
Heel Ultrasound Predicts Osteoporosis Risk
News from the RSNA Journal Radiology
June 24, 2008
Simple Ultrasound Exam May Predict Osteoporosis Risk At A Glance
An ultrasound exam of the heel may be able to predict if a woman is at heightened risk for fractures due to osteoporosis, according to a new multicenter study being published in the July issue of the journal Radiology. Along with certain risk factors, including age or recent fall, radiation-free ultrasound of the heel may be used to better select women who need further bone density testing, such as a dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) exam.
In the three-year multicenter study, 6,174 women age 70 to 85 with no previous formal diagnosis of osteoporosis were screened with heel-bone quantitative ultrasound (QUS), a diagnostic test used to assess bone density. QUS was used to calculate the stiffness index, which is an indicator of bone strength, at the heel. Researchers added in risk factors such as age, history of fractures or a recent fall to the results of the heel-bone ultrasound to develop a predictive rule to estimate the risk of fractures.
In the group of higher risk women, 290 (6.1 percent) developed fractures whereas only 27 (1.8 percent) of the women in the lower risk group developed fractures. Among the 66 women who developed a hip fracture, 60 (90 percent) were in the higher risk group.
The results show that heel QUS is not only effective at identifying high-risk patients who should receive further testing, but also may be helpful in identifying patients for whom further testing can be avoided.
Wednesday, December 3, 2008
RSS Feeder Added
I have added a RSS feeder at the top right of my blog so that you may subscribe to posts and comments. Just click on either posts or comments or both and select your RSS reader.
Monday, November 24, 2008
Petition FDA To Add Strontium Citrate
I have just asked the FDA to consider adding strontium citrate to their Medline supplement index, which is a list of approved supplements. If you would like to email the FDA, click here: http://vm.cfsan.fda.gov/~dms/qa-top.html
Tuesday, November 4, 2008
Effect Of Strontium on DEXA Scan
The presence of strontium in bone influences bone mineral density (BMD) and bone mineral content (BMC) measurements by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA). DEXA scans are usually read based on calcium as the main component of bone. Since strontium is heavier than calcium, its presence in bone will change the results of the scan.
When you go for your next DEXA scan, be sure to inform the radiologist, in writing, about your daily dose of strontium and how long you have been taking it. He can make a correction, or at least note on your results, that you have been taking strontium. Without an adjustment in the interpretation, BMD can be read as artificially high. You might be wise to give the clinician a copy of "Strontium DEXA Scan Effect," which you can print out at www.osteopenia3.com/Strontium-dexa-scan.html.
When you go for your next DEXA scan, be sure to inform the radiologist, in writing, about your daily dose of strontium and how long you have been taking it. He can make a correction, or at least note on your results, that you have been taking strontium. Without an adjustment in the interpretation, BMD can be read as artificially high. You might be wise to give the clinician a copy of "Strontium DEXA Scan Effect," which you can print out at www.osteopenia3.com/Strontium-dexa-scan.html.
Monday, September 1, 2008
Strontium Malonate
Osteologix, Inc., a specialty biopharmaceutical company headquartered in San Francisco, CA, announced in May, 2008, that the FDA has accepted its investigational new drug (IND) application for NB S101 (strontium malonate) to treat and prevent osteoporosis. See links to three articles on this topic at the end of this blog.
Monday, August 11, 2008
Men And Young Women With Osteoporosis
Mention osteoporosis to most people and they automatically think of women, especially older women, but men and young women can also have brittle bones. According to Dr. Isadore Rosenfeld's article in Parade (May 18, 2008, page 8), two million men is the U.S.A. have the disease, and 12 million more are at risk. I haven't found statistics for young women, but I have read blog posts from several women in their 20's and 30's with osteoporosis.
Causes include:
- Steroids taken to treat asthma or arthritis
- Long-term use of antacids containing aluminum
- Low levels of sex hormones (Hysterectemies in women can cause this.)
- Too much thyroid hormone
- Smoking
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Lack of exercise
- Inadequate dietary calcium
- Heredity
- Lactation (Nursing mothers lose calcium.)
Labels:
alcohol,
antacids containing aluminum,
calcium,
exercise,
heredity,
men,
osteoporosis,
sex hormones,
smoking,
steroids,
young women
Thursday, June 19, 2008
Why I No Longer Take Fosamax
I took Fosamax 70 mg once weekly for seven months before getting off due to intolerable side effects beginning after four months. The worst problems were vertigo and dizziness, which came on suddenly. I woke up one morning and when I tried to get out of bed, I felt like I was falling. I had to call my husband to assist me to the bathroom. Although these symptoms became less severe, I never regained my equilibrium while on Fosamax and was unable to exercise on the floor due to vertigo when I lay flat. I also experienced heart palpitations,extreme coldness, and general malaise about two hours after taking my weekly dose. I now wonder if I was having atrial fibrillation, another serious side effect of Fosamax. I am so glad I got off it!
I gave my body a month to clear out the drug and then I began taking strontium citrate 680 mg once daily. I feel well again and began this blog to relate my progress and get comments from others.
I gave my body a month to clear out the drug and then I began taking strontium citrate 680 mg once daily. I feel well again and began this blog to relate my progress and get comments from others.
Labels:
atrial fibrillation,
coldness,
dizziness,
heart palpitations,
malaise,
vertigo
Wednesday, May 21, 2008
Availability Of Protelos In U.S.
Is your company seeking approval of Protelos (strontium ranelate)for osteoporosis in the United States of America? If so, at what stage in the process is it?
BoneLady
Thank you for your interest for Protelos. Protelos is registered in 84 countries worldwide but has not yet been filed to the FDA and thus, for the time being, it is not possible to give you any indication on availability date in the USA.
Sincerely,
M. Rebuffé-Scrive
Scientific Director Servier International Canada, USA, Northern, Central & Eastern Europe
BoneLady
Thank you for your interest for Protelos. Protelos is registered in 84 countries worldwide but has not yet been filed to the FDA and thus, for the time being, it is not possible to give you any indication on availability date in the USA.
Sincerely,
M. Rebuffé-Scrive
Scientific Director Servier International Canada, USA, Northern, Central & Eastern Europe
Labels:
FDA,
osteoporosis,
Protelos,
strontium ranelate
Tuesday, May 20, 2008
Alternative Medicine For Osteoporosis
Strontium citrate is an excellent alternative medicine for osteoporosis treatment. Instead of poisoning your body with drugs such as Fosamax, take strontium, a naturally occurring mineral present in water, food, and the human skeleton in trace amounts. Studies show that strontium promotes bone formation and decreases bone resorption (loss), leading to higher bone density.
Friday, May 2, 2008
Strontium And Arthritis
Did you know that there is some evidence that strontium may improve cartilage metabolism in osteoarthritis? An in vitro study performed by the Bone and Cartilage Metabolism Research Unit, University Hospital, Liege, Belgium, suggests strontium promotes cartilage growth. Clinical testing is needed in this area. For more information on this subject, go to Strontium For Osteoporosis and Arthritis in my links section.
Labels:
arthritis,
cartilage,
osteoarthritis,
strontium
Tuesday, April 22, 2008
Strontium For Osteoporosis
I took Fosamax 70 mg once weekly for seven months until I could no longer tolerate the side effects. I waited a month before starting a regimen of strontium citrate 680 mg once daily. Please comment with your experiences taking strontium or if you would like more information about it.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
Wandering Skeleton

Artist: Joel Hoekstra
Osteoporotic Bone
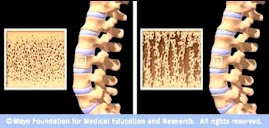
Source: www.mayoclinic.com
How Strontium Builds Bones
Strontium is a mineral that tends to accumulate in bone. Studies have shown that oral doses of strontium are a safe and effective way to prevent and reverse osteoporosis. Doses of 680 mg per day appear to be optimal. See my "For More Information About Strontium" links section.
Osteoporosis is caused by changes in bone production. In healthy young bones there is a constant cycle of new bone growth and bone removal. With age, more bone is removed and less new bone is produced. The bones become less dense and thus more fragile.
Scientists believe that strontium works in two ways. It may stimulate the replication of pre-osteoblasts, leading to an increase in osteoblasts (cells that build bone). Strontium also directly inhibits the activity of osteoclasts (cells that break down bone). The result is stronger bones.
When taking strontium, be sure to take 1200 mg calcium, 1000 IU vitamin D3, and 500 mg magnesium daily. It is best to take strontium late at night on an empty stomach. Calcium and strontium may compete with each other for absorption if taken together.
Osteoporosis is caused by changes in bone production. In healthy young bones there is a constant cycle of new bone growth and bone removal. With age, more bone is removed and less new bone is produced. The bones become less dense and thus more fragile.
Scientists believe that strontium works in two ways. It may stimulate the replication of pre-osteoblasts, leading to an increase in osteoblasts (cells that build bone). Strontium also directly inhibits the activity of osteoclasts (cells that break down bone). The result is stronger bones.
When taking strontium, be sure to take 1200 mg calcium, 1000 IU vitamin D3, and 500 mg magnesium daily. It is best to take strontium late at night on an empty stomach. Calcium and strontium may compete with each other for absorption if taken together.
For More Information about Strontium
- A Dose-response Study With Strontium Malonate
- A Review of the latest insights into the mechanism of action of strontium in bone
- Antifracture Efficacy Over 10 Years With Strontium Ranelate
- Combination of Micronutrients for Bone (COMB) Study: Bone Density after Micronutrient Intervention
- Echolight REMS Scan of Young, Normal Female
- Effect of bone strontium on BMD measurements
- Effect of Lumbar Scoliosis on DXA Results
- Effects of SrR on Calcium Metabolism
- Effects of strontium ions on growth and dissolution of hydroxyapatite and on bone mineral detection
- Influence of strontium on bone mineral density and bone mineral content measurements by dual X-ray absorptiometry
- Interpretation of BMD Scans in Patients Stopping Strontium
- Melatonin-micronutrients Osteopenia Treatment Study (MOTS)
- National Osteoporosis Foundation
- Osteoporosis And Bone Physiology
- Post-Marketing Assessment of the Safety of Strontium Ranelate
- PubMed Abstract On The SOTI Study
- PubMed Abstract On The TROPOS Study
- Strontium ranelate Aristo
- Strontium Ranelate For Spinal Osteoarthritis
- Strontium: Breakthrough Against Osteoporosis
- Summary Safety Review - Strontium
- The Effects of Strontium Ranelate on the Risk of Vertebral Fracture in Women with Postmenopausal Osteoporosis
- The Influence of Strontium on Bone Tissue Metabolism and Its Application in Osteoporosis Treatment
- Thirteen Key Diagnostic Tests