The following abstract was published on Osteoporosis International (2012) 23: (Supplement 2):S85–S386.
Abstract P471, Pages S266-S267
Didier Hans1, Marc-Antoine Krieg1, Olivier Lamy1, Dieter Felsenberg2
1Lausanne University Hospital Center of Bone Diseases, Bone and Joints Department, Lausanne, Switzerland, 2Charité Campus Benjamin Franklin, Klinik und Poliklinik für Radiologue und Muklearmedizin, Berlin, Germany
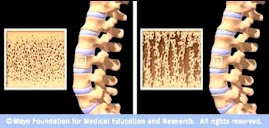
Objective(s): Trabecular Bone Score (TBS, Med-Imaps, France) is an index of bone architecture independent of BMD calculated by quantifying local variations in grey level from anteroposterior spine DXA scan and reported to be associated with fracture in prior case-control and prospective studies1. We compared the effects of strontium ranelate (SrRan) and alendronate (ALN) on spine architecture patterns as assessed by TBS in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis.
Material & Methods: A post hoc analysis was performed on DXAs (Hologic and GE Lunar Devices) from 79 women out of 189 included in a double blind, double dummy study and randomized to SrRan 2 g/day or ALN 70 mg/week during 2 years2. Spine TBS parameters were assessed by TBS iNsight (v1.9) at the spine after 12 and 24 months of treatment. We applied ISCD rules for individual vertebrae exclusion independently for BMD and TBS, respectively. Since duplicate measurements were performed at baseline, precision were calculated as CV%.
Results: Baseline characteristics (mean ± SD) were similar between groups in term of age, 69.2 ± 4.4 years; BMI, 23.8±4.4 kg/m2; L1-L4 T-score, -2.9±0.9 and TBS 1.230 ± 0.09. As expected, the correlation between Spine BMD and TBS was very low with r2 = 0.12. Precision errors were 1.1% and 1.6% for spine BMD and TBS, respectively. Over 1 and 2 years, L1-L4 BMD increased significantly by 5.6% and 9% in SrRan group and by 5.2% and 7.6%, respectively in ALN group. Similarly, spine TBS increased by 2.3% (p < 0.001) and 3.1% (p < 0.001) in SrRan group and by 0.5% (ns) and 1.0% (ns) respectively in ALN group with a significant between-group difference in favor of SrRan (p = 0.04 and p = 0.03). There were no correlation between delta BMD and TBS at 1 year or at 2 years. The two treatments were well tolerated.
Conclusion(s): SrRan has greater effects on bone architecture index at the spine compared to alendronate in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis after 2-year treatment. These results consolidate previous studies supporting a benefit of SrRan on bone architecture.
References: 1. Hans D. et al. J Bone Miner Res 2011;26:2762.
2. Felsenberg D. et al. Osteoporos Int 2011;22(suppl. 1):S102.
https://sci-hub.se/https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-012-1928-7


No comments:
Post a Comment