- A higher-protein diet that emphasizes lean meats and low-fat dairy foods as sources of protein and calcium can mean weight loss without bone loss. The evidence is in bone scans taken throughout a new University of Illinois study.
This is an important finding because many people, especially women in mid-life, are concerned with both obesity and osteoporosis. However, treating obesity often increases risk for osteoporosis because many people lose bone mass when they lose weight.
The research compared the results of a high-protein, dairy-intensive diet with a conventional weight-loss diet based on the food-guide pyramid.
Study co-author Donald Layman, a U of I professor of nutrition, has previously reported that protein-rich weight-loss diets preserve muscle mass, help lower blood sugar and lipids, and improve body composition by targeting weight carried in the abdomen.
In the recent study, Layman's diet prescribed approximately 30 percent of all calories from protein, with an emphasis on lean meats and low-fat dairy products.
The scientists recruited and randomized 130 middle-aged, overweight persons at two sites--the U of I and Pennsylvania State University. Participants then followed either the higher-protein weight-loss diet or a conventional higher-carbohydrate weight-loss diet based on the food-guide pyramid for four months of active weight loss followed by eight months of weight maintenance.
Essentially, lean meats and low-fat milk, cheese, yogurt, etc. were substituted for some of the high-carbohydrate foods in the food-pyramid diet. Participants also ate five servings of vegetables and two to three servings of fruit each day.
Bone mineral content and density were measured with DXA scans of the whole body, lumbar spine, and hip at the beginning of the study, at four months, at eight months, and at the end of the 12-month period.
In the higher-protein group, bone density remained fairly stable, but bone health declined over time in the group that followed the conventional higher-carbohydrate diet. A statistically significant treatment effect favored the higher-protein diet group.
The combination and/or interaction of dietary protein, calcium from dairy, and the additional vitamin D that fortifies dairy products appears to protect bone health during weight loss.
Because higher-protein diets have been associated with elevated urinary calcium levels, some scientists have feared that these diets cause bone demineralization.
The U of I team measured these levels at the beginning and eight months into the study. Although the researchers did note increased amounts of urinary calcium in the higher-protein group, they attributed the source of the increased calcium to improved intestinal absorption of calcium rather than bone loss.
Other recent studies using radio-labeled calcium have shown that the higher urinary calcium levels associated with higher-protein diets are not coming from bone as some researchers had believed.
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2008/06/080605113006.htm
Human Skeleton

WELCOME TO STRONTIUM FOR BONES BLOG
Visitors to my blog can leave comments or ask questions and can remain anonymous, if they wish. Their comments are relayed to my g-mail inbox. Below each post, the number of comments for that post is cited and underlined because it is a link. By clicking on that link below any post, a window opens so that a visitor can leave a comment. Ideally, visitors leave comments on posts most relevant to their comments. All comments to my posts are moderated by me.
Browse the posts and visit the link library of references.
Saturday, June 19, 2021
How to Lose Weight Without Losing Bone
Thursday, June 17, 2021
Taking Calcium and Magnesium Together
I always grin to myself when I read about not taking calcium and magnesium together because the two are together in many foods. It is true that if you take a large amount of calcium (e.g., 500 mg) with a smaller amount of magnesium (e.g., 250 mg), you will not absorb as much of the magnesium, but you will probably absorb the calcium better. We need magnesium to absorb and metabolize calcium and vitamin D. Below is a chart of calcium and magnesium in foods.
Calcium and Magnesium in Foods (milligrams)
Collards (1 cup, boiled)
268 Ca
40 Mg
Orange juice, calcium-fortified (1 cup)
349 Ca
27 Mg
Oatmeal, fortified instant (1 packet)
98 Ca
36 Mg
Figs, dried (10 medium)
136 Ca
57 Mg
Tofu, calcium-set (1/2 cup)
861 Ca
73 Mg
Spinach (1 cup, boiled)
245 Ca
157 Mg
Soybeans (1 cup, boiled)
261 Ca
108 Mg
White beans (1 cup, boiled)
161 Ca
113 Mg
Mustard greens (1 cup, boiled)
165 Ca
18 Mg
Navy beans (1 cup, boiled)
128 Ca
96 Mg
Great northern beans (1 cup, boiled)
120 Ca
88 Mg
Black turtle beans (1 cup, boiled)
102 Ca
91 Mg
Swiss chard (1 cup, boiled)
102 Ca
152 Mg
Broccoli (1 cup, boiled)
62 Ca
33 Mg
Kale (1 cup boiled)
94 Ca
23 Mg
English muffin
101 Ca
21 Mg
Butternut squash (1 cup, boiled)
84 Ca
60 Mg
Pinto beans (1 cup, boiled)
79 Ca
86 Mg
Chick peas (1 cup, canned)
109 Ca
61 Mg
Sweet potato (1 cup, boiled)
76 Ca
54 Mg
Green beans (1 cup, boiled)
55 Ca
22 Mg
Barley (1 cup)
61 Ca
245 Mg
Brussels sprouts (8 sprouts)
60 Ca
34 Mg
Navel orange (1 medium)
60 Ca
15 Mg
Raisins (2/3 cup)
54 Ca
35 Mg
Source: U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service. 2011. USDA National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference, Release 26.
*Nutrient Data Laboratory Home Page, http://ndb.nal.usda.gov/
https://www.pcrm.org/good-nutrition/nutrition-information/health...
Wandering Skeleton

Artist: Joel Hoekstra
Osteoporotic Bone
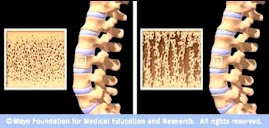
Source: www.mayoclinic.com
How Strontium Builds Bones
Osteoporosis is caused by changes in bone production. In healthy young bones there is a constant cycle of new bone growth and bone removal. With age, more bone is removed and less new bone is produced. The bones become less dense and thus more fragile.
Scientists believe that strontium works in two ways. It may stimulate the replication of pre-osteoblasts, leading to an increase in osteoblasts (cells that build bone). Strontium also directly inhibits the activity of osteoclasts (cells that break down bone). The result is stronger bones.
When taking strontium, be sure to take 1200 mg calcium, 1000 IU vitamin D3, and 500 mg magnesium daily. It is best to take strontium late at night on an empty stomach. Calcium and strontium may compete with each other for absorption if taken together.
For More Information about Strontium
- A Dose-response Study With Strontium Malonate
- A Review of the latest insights into the mechanism of action of strontium in bone
- Antifracture Efficacy Over 10 Years With Strontium Ranelate
- Combination of Micronutrients for Bone (COMB) Study: Bone Density after Micronutrient Intervention
- Echolight REMS Scan of Young, Normal Female
- Effect of bone strontium on BMD measurements
- Effect of Lumbar Scoliosis on DXA Results
- Effects of SrR on Calcium Metabolism
- Effects of strontium ions on growth and dissolution of hydroxyapatite and on bone mineral detection
- Influence of strontium on bone mineral density and bone mineral content measurements by dual X-ray absorptiometry
- Interpretation of BMD Scans in Patients Stopping Strontium
- Melatonin-micronutrients Osteopenia Treatment Study (MOTS)
- National Osteoporosis Foundation
- Osteoporosis And Bone Physiology
- Post-Marketing Assessment of the Safety of Strontium Ranelate
- PubMed Abstract On The SOTI Study
- PubMed Abstract On The TROPOS Study
- Strontium ranelate Aristo
- Strontium Ranelate For Spinal Osteoarthritis
- Strontium: Breakthrough Against Osteoporosis
- Summary Safety Review - Strontium
- The Effects of Strontium Ranelate on the Risk of Vertebral Fracture in Women with Postmenopausal Osteoporosis
- The Influence of Strontium on Bone Tissue Metabolism and Its Application in Osteoporosis Treatment
- Thirteen Key Diagnostic Tests