Bone 2013
Strontium ranelate is an approved pharmacotherapy for osteoporosis in Europe and Australia,
but not in Canada or the United States. Strontium citrate, an alternative
strontium salt, however, is available for purchase over-the-counter as a
nutritional supplement. The effects of strontium citrate on bone are largely
unknown.
The study's objectives were (1) to quantify bone strontium accumulation in female Sprague Dawley rats administered strontium citrate (N=7) and compare these levels to rats administered strontium ranelate (N=6) and vehicle (placebo) (N=6) over 8 weeks, and (2) to verify an in vivo X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (XRF) system for measurement of bone strontium in the rat. Daily doses of strontium citrate and strontium ranelate were determined with the intention to achieve equivalent amounts of elemental strontium. However, post-hoc analyses of each strontium compound conducted using energy dispersive spectrometry microanalysis revealed a higher elemental strontium concentration in strontium citrate than strontium ranelate.
The study's objectives were (1) to quantify bone strontium accumulation in female Sprague Dawley rats administered strontium citrate (N=7) and compare these levels to rats administered strontium ranelate (N=6) and vehicle (placebo) (N=6) over 8 weeks, and (2) to verify an in vivo X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (XRF) system for measurement of bone strontium in the rat. Daily doses of strontium citrate and strontium ranelate were determined with the intention to achieve equivalent amounts of elemental strontium. However, post-hoc analyses of each strontium compound conducted using energy dispersive spectrometry microanalysis revealed a higher elemental strontium concentration in strontium citrate than strontium ranelate.
Bone strontium levels were measured at baseline and
8 weeks follow-up using a unique in vivo XRF technique previously used in
humans. XRF measurements were validated against ex vivo measurements of bone
strontium using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Weight gain in
rats in all three groups was equivalent over the study duration. A two-way
ANOVA was conducted to compare bone strontium levels amongst the three groups.
Bone strontium levels in rats administered strontium citrate were significantly
greater than in rats administered strontium
ranelate and vehicle. ANCOVA analyses were performed with Sr dose as a
covariate to account for differences in strontium dosing. The ANCOVA revealed
differences in bone strontium levels between the strontium groups were not
significant, but that bone strontium levels were still very significantly
greater than vehicle.


2 comments:
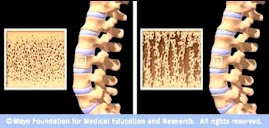
It is very hard for me to understand what osteoporosis is. I've never really had bad bones. My dad has it and I really want to help him but, I don't know how. http://www.lynchburggynecology.com
William Walker,
The word osteoporosis literally means "porous bones." It occurs when bones lose an excessive amount of their protein and mineral content, particularly calcium. If you really want to help your father, read my blog and tell him about the supplement, strontium citrate. Other supplements that are also important for bones include calcium (taken at least 3 hours away from strontium), magnesium, and vitamin D3.
I don’t know anything about Lynchburg Gynecology and do not endorse their services.
Post a Comment