Human Skeleton

WELCOME TO STRONTIUM FOR BONES BLOG
Have you experienced negative, and even dangerous, side effects from Fosamax (alendronate), Boniva (ibandronate), Actonel (risedronate), Reclast (zoledronic acid), Prolia (denosumab), Forteo (teriparatide), Tymlos (abaloparatide), or other drugs prescribed for osteoporosis? If you have, then rest assured there is a safe, effective treatment for this condition. Strontium, primarily in the form of strontium citrate, is taken orally once a day.
Visitors to my blog can leave comments or ask questions and can remain anonymous, if they wish. Their comments are relayed to my g-mail inbox. Below each post, the number of comments for that post is cited and underlined because it is a link. By clicking on that link below any post, a window opens so that a visitor can leave a comment. Ideally, visitors leave comments on posts most relevant to their comments. All comments to my posts are moderated by me.
Browse the posts and visit the link library of references.
Visitors to my blog can leave comments or ask questions and can remain anonymous, if they wish. Their comments are relayed to my g-mail inbox. Below each post, the number of comments for that post is cited and underlined because it is a link. By clicking on that link below any post, a window opens so that a visitor can leave a comment. Ideally, visitors leave comments on posts most relevant to their comments. All comments to my posts are moderated by me.
Browse the posts and visit the link library of references.
Tuesday, April 24, 2012
Interpretation of BMD Scans in Patients Stopping Strontium Ranelate Treatment
“The oral administration of strontium ranelate causes a clinically significant overestimation of BMD because of the high attenuation of X-rays by strontium atoms in bone." GM Blake and I. Fogelman “performed a theoretical study to calculate the long-term effect of strontium treatment on BMD and establish the duration of past treatment for which the remaining bone strontium content (BSC) has a negligible effect on BMD.” “Estimates of the strontium BMD artefact after treatment has stopped were performed on the assumption that the BSC effect accounts for 75% of the total measured BMD change at 3 years.”
“If 75% of the BMD changes are explained by BSC, in the average patient, 3-year treatment leads to a spine BMD artefact of 11.2%, decreasing to 3.8% 10 years after stopping treatment. The BMD artefacts at the total hip and femoral neck sites are smaller by factors of 0.65 and 0.53, respectively.” “On average, 6-month treatment is required for the spine BMD artefact to exceed 3%, the figure adopted as the maximum BMD change caused by bone strontium that has a negligible effect on scan interpretation.”
The researchers concluded that “strontium ranelate treatment lasting for > 6 months can affect BMD measurements for many years afterward.”
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16939400
J Bone Miner Res. 2006 Sep;21(9):1417-24.
Thursday, April 5, 2012
Minimum Effective Doses of Strontium
The aim of the PREVOS study
(PREVention Of early postmenopausal bone loss by Strontium ranelate) and the
STRATOS study (STRontium Administration for Treatment of OSteoporosis) was to
determine the minimum dose at which strontium ranelate (SR) is effective in,
respectively, the prevention of bone loss in early postmenopausal
nonosteoporotic women and the treatment of postmenopausal vertebral
osteoporosis.
The minimum dose at which SR is
effective in preventing bone loss in early postmenopausal nonosteoporotic women
and in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis is 1 g/day and 2 g/day,
respectively.
Strontium ranelate phase 2 dose-ranging
studies: PREVOS and STRATOS studies, J. Y. Reginster and P. J.
Meunier, Osteoporosis
International, Volume
14, Supplement 3, 56-65, DOI:
10.1007/s00198-002-1349-0
The chemical structure of strontium ranelate is
composed of two atoms of stable strontium combined with organic ranelic acid.
Strontium is the bone active component and makes up 34% by weight of the whole
molecule, so each 2 g dose of strontium ranelate delivers 680 mg of elemental
strontium.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
Wandering Skeleton

Artist: Joel Hoekstra
Osteoporotic Bone
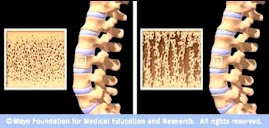
Source: www.mayoclinic.com
How Strontium Builds Bones
Strontium is a mineral that tends to accumulate in bone. Studies have shown that oral doses of strontium are a safe and effective way to prevent and reverse osteoporosis. Doses of 680 mg per day appear to be optimal. See my "For More Information About Strontium" links section.
Osteoporosis is caused by changes in bone production. In healthy young bones there is a constant cycle of new bone growth and bone removal. With age, more bone is removed and less new bone is produced. The bones become less dense and thus more fragile.
Scientists believe that strontium works in two ways. It may stimulate the replication of pre-osteoblasts, leading to an increase in osteoblasts (cells that build bone). Strontium also directly inhibits the activity of osteoclasts (cells that break down bone). The result is stronger bones.
When taking strontium, be sure to take 1200 mg calcium, 1000 IU vitamin D3, and 500 mg magnesium daily. It is best to take strontium late at night on an empty stomach. Calcium and strontium may compete with each other for absorption if taken together.
Osteoporosis is caused by changes in bone production. In healthy young bones there is a constant cycle of new bone growth and bone removal. With age, more bone is removed and less new bone is produced. The bones become less dense and thus more fragile.
Scientists believe that strontium works in two ways. It may stimulate the replication of pre-osteoblasts, leading to an increase in osteoblasts (cells that build bone). Strontium also directly inhibits the activity of osteoclasts (cells that break down bone). The result is stronger bones.
When taking strontium, be sure to take 1200 mg calcium, 1000 IU vitamin D3, and 500 mg magnesium daily. It is best to take strontium late at night on an empty stomach. Calcium and strontium may compete with each other for absorption if taken together.
For More Information about Strontium
- A Dose-response Study With Strontium Malonate
- A Review of the latest insights into the mechanism of action of strontium in bone
- Antifracture Efficacy Over 10 Years With Strontium Ranelate
- Combination of Micronutrients for Bone (COMB) Study: Bone Density after Micronutrient Intervention
- Echolight REMS Scan of Young, Normal Female
- Effect of bone strontium on BMD measurements
- Effect of Lumbar Scoliosis on DXA Results
- Effects of SrR on Calcium Metabolism
- Effects of strontium ions on growth and dissolution of hydroxyapatite and on bone mineral detection
- Influence of strontium on bone mineral density and bone mineral content measurements by dual X-ray absorptiometry
- Interpretation of BMD Scans in Patients Stopping Strontium
- Melatonin-micronutrients Osteopenia Treatment Study (MOTS)
- National Osteoporosis Foundation
- Osteoporosis And Bone Physiology
- Post-Marketing Assessment of the Safety of Strontium Ranelate
- PubMed Abstract On The SOTI Study
- PubMed Abstract On The TROPOS Study
- Strontium ranelate Aristo
- Strontium Ranelate For Spinal Osteoarthritis
- Strontium: Breakthrough Against Osteoporosis
- Summary Safety Review - Strontium
- The Effects of Strontium Ranelate on the Risk of Vertebral Fracture in Women with Postmenopausal Osteoporosis
- The Influence of Strontium on Bone Tissue Metabolism and Its Application in Osteoporosis Treatment
- Thirteen Key Diagnostic Tests